

October 13, 2020
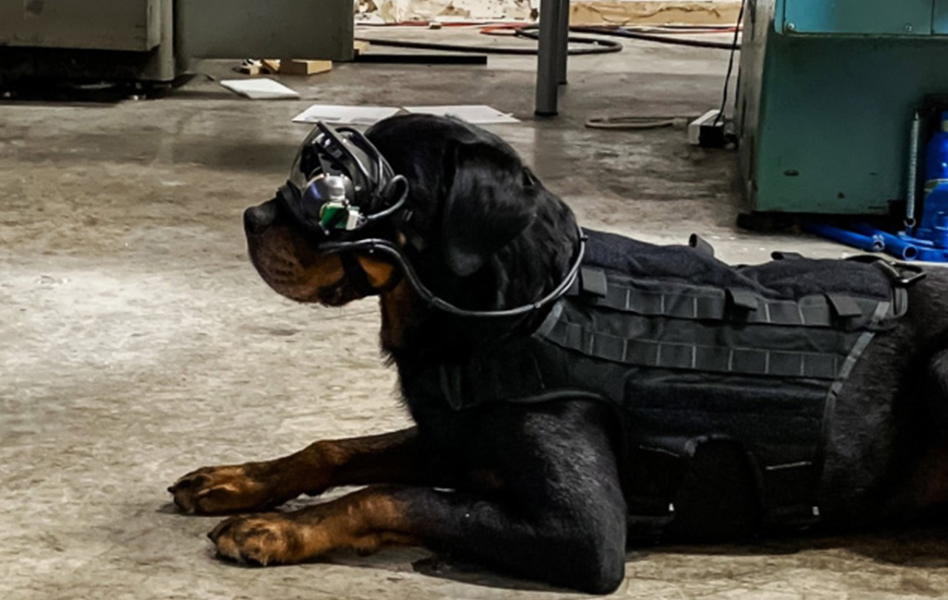

It’s true that dogs are a man's best friend, this is especially true with the armed forces. Military working dogs are used for scouting and finding explosives, along with other reconoscence missions. It is essential that these dogs get commands from their handler to keep them safe and to help the dog along with the mission.
Just think, giving Augmented Reality technology to working dogs sounds like a great idea. One of the best things about using AR to guide military dogs is that they are already wearing military goggles for eye protection. The Army Research Office, part of the U.S Army Combat Capabilities Development is working on this new technology. AR is being developed for dogs with the aim of commanders being able to help get their companions where they need to be. This also helps soldiers keep out of harm's way as they can be further distanced from their canine companion.
Not only this but it’s bridging the communication gap between human and canine. The need for better communication between human and canine is well known and AR can possibly bridge this gap.
An example is when the canine cant see their trainer, they might lose focus and become disoriented and off task. This gives a permanent link between canine and human.
Dr. A.J. Peper founded Command Sight in 2017, after identifying the need for better human-animal communication on the field. Peper was surprised by initial feedback from his proof of concept, “the system could fundamentally change how military canines are deployed in the future.”
The AR tech that is being trialed is specially designed to fit the canine's shape and needs. There is a visual indicator that shows the dog directions as to where he needs to go, he is reacting to visual cues in his goggles.
The handler now has the ability to see exactly what the dog sees through the AR headset
“Augmented reality works differently for dogs than for humans,” said Dr. Stephen Lee, an ARO senior scientist. “AR will be used to provide dogs with commands and cues; it’s not for the dog to interact with it like a human does. This new technology offers us a critical tool to better communicate with military working dogs.”
For now, the prototype used is wired, similar to being on a leash for the dog. Researchers are currently developing how to do this wirelessly for their next stage of development
“We are still in the beginning research stages of applying this technology to dogs, but the results from our initial research are extremely promising,” Peper states. “Much of the research to date has been conducted with my rottweiler, Mater. His ability to generalize from other training to working through the AR goggles has been incredible. We still have a way to go from a basic science and development perspective before it will be ready for the wear and tear our military dogs will place on the units.”
The research conducted focuses on how the canine eye perceives the world.
“We will be able to probe canine perception and behavior in a new way with this tool,” Lee said.
Military working dogs are currently directed by hand signals or laser pointers, which works well when there is line of sight. The issue arises when the canine can no longer see the handler, this can become a safety issue not only for the canine, but the handler too.
Equipping Augmented reality goggles to the worker dog makes sense doesn't it? This could offer special forces and their canines companions a new way to communicate.
“The military working dog community is very excited about the potential of this technology,” Lee said. “This technology really cuts new ground and opens up possibilities that we haven’t considered yet.”
It’s not a huge step to put AR technology into what they are already wearing. It makes adoption of this technology cheap and effective. It’s set to greatly improve communication between canine and handler.
“Even without the augmented reality, this technology provides one of the best camera systems for military working dogs,” Lee states. “Now, cameras are generally placed on a dog’s back, but by putting the camera in the goggles, the handler can see exactly what the dogs sees and it eliminates the bounce that comes from placing the camera on the dog’s back.”
The researchers have planned to spend another two years refining the product and making it wireless. The Army Research Office is proving additional funding for the next phase of development.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

October 6, 2020

Many say that the best learning happens on the job, with this being very true as you get a practical sense of how you are going to perform your task. The best situation for someone who is starting their new job is to practice physically but without any risks. VR offers this and with the right software and devices it’s possible to simulate a students work environment with a great degree of accuracy.
Google came up with a test by creating two teams to compete for making the best cup of espresso. One team learnt their skills by watching training videos on YouTube, the other used VR headsets to learn. Neither team made an exceptional cup of espresso, but the VR group certainly made fewer mistakes and also brewed their cup in a quicker manner.
One industry where VR is shining is in the construction industry where VR is used to train employees in a safe, effective way. Hong Kong-based Gammon Construction Ltd. and San Francisco-based Bechtel are currently using VR in their training programs. Using wearable technology, the workers can train in a safe environment without the risk of injury, making the training process more enjoyable.
“VR creates a much more immersive and engaging environment for training the workforce,” said Chris Bunk, HCS chief operating officer.
Four training modules have already been created states Bunk, and a new module is launched about every six weeks. The training modules cover a range of topics such as forklift training, scaffolding and metal worker training and hazard identification training. All being undertaken in complete safety.
Bunk said “People go up on a high rise doing iron work and when they get out on the beam for the first time the heights get to them more than they expected and they may feel like they have to cling to the beam or use their fall protection,” and also added “We give them the opportunity to get acclimated to that environment beforehand.”
“The course has virtual hazards like somebody walking up right in front of you,” added bunk “That’s the type of thing that’s very difficult to simulate in real training because you don’t want someone to accidentally get hit.”
Something really promising about VR training is its ability to give the user an enjoyable experience. “Everyone is very engaged, sometimes even friendly competitive,” Bunk said. “You go from people fumbling with their phones, half falling asleep from archaic PowerPoints to something where people are getting up, engaged and enriched in the material.”
Word is spreading throughout the construction industry about the benefits of training employees with VR. “It’s to the point where training is now something that someone is asking for which is very rare in a lot of industries” Bunk states.
While VR hasn’t saturated the construction industry yet, like it has in the health care sector, it’s plain to see it’s coming fast for construction training.
A chief training officer Lynne Bamford at Northshore University Health System in Chicago said that there is potential for VR training, but also a hesitancy to spend money, as revenues across its health care industry has declined. Budgeting for training as a whole is an ongoing balancing act. “Our budgets are in really bad shape. So it’s very difficult to say I want to spend more money on a virtual reality training session” she explains.
Bamford stated that she could envisage VR being used for simulation training, to acclimatize people to their future setting, simulate real operations thus developing employee confidence. However she is skeptical regarding its use in more interactive situations.
Despite this Bunk says that VR holds much promise as it continues to evolve and mature. He predicts that VR is going to become more commonplace in industrial training over the next few years, resulting in more efficient and safer training.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

March 24, 2020

Google and NVIDIA’s Super-resolution scaling AI are real winners, turning low quality images into more detailed ones, proving this software is game changing. Oculus have shown great interest and plan on using it themselves in the not too distant future.
After some research Facebook’s AI division have found a way to provide developers with more rendering power with a simple software update. It gives up to 67% more rendering power and is suitable for mobile VR hardware. Though implementation of any sort of image rendering AI can be complex and have a range of issues to address. This latest update sees clear improvements in performance for the current generation of VR hardware.
A document from Facebook AI researchers states that they are using a “super-resolution” algorithm to turn poor quality images into higher resolution, clearer images. This means for example Oculus Quest apps can be rendered at 70% of their current resolution which in turn drastically increases performance of the app allowing higher frame rates for a better experience. This super-resolution algorithm will take lower resolution images and convert them into new images utilizing the devices mobile processing architecture. The end result is much sharper and more detailed images, without using as much processing power as it normally would rendering high quality frames.
Using AI to improve image quality is nothing new, NVIDIA used its own AI-upscaling algorithm for Shield TV last year and google used it’s Super Res Zoom on the Pixel 3’s camera back in 2018. This technology is especially good for older, slower mobile chipsets like the Snapdragon 835. It’s also a huge benefit for developers who wish to port their PC VR titles over to the Quest, As well as making it easier to develop apps to run across multiple platforms.
Once, this concept of turning low quality images into high resolution ones was just stuff of science fiction. But with advances in AI, what once seemed impossible has become reality. Facebook’s super-resolution algorithm isn’t too different from previous algorithms of its kind. It teaches machines to detect common objects and then the AI imagines how the full object is meant to look. NVIDIA’s developed a similar AI algorithm for its RTX line of graphics cards to enhance images while not suffering much of a loss in performance.
For now, while there is much anticipation, there is no set timeline for rolling out the updates for Oculus Quest, or for any headsets. Dynamic Fixed Foveated Rendering was added to Oculus development kit last year, which greatly improved the performance of the Quest’s apps with no real loss in visual quality. We hope to see this update rolled out sooner rather than later.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

December 10, 2019

As Augmented and Virtual reality technologies mature, they are becoming a viable option for enterprise training. However there is still a way to go before these technologies become commonplace in most business scenarios.
J.P. Gownder, vice president at Forrester states, "Right now, we mostly remain in the early testing phase for AR and VR, but employee training is becoming a more common scenario"
Walmart and UPS are a couple of companies who have rolled out VR training programs. This is helping their new employees master their jobs faster and with higher quality and safety. At UPS, new drivers will use VR headsets to simulate city driving conditions during training. Large mining companies are using AR to help workers identify and fix problems with equipment, in factories or out in the field.
VR has had a huge impact on the customer side of things mostly due to gaming. Enterprise AR adoption is ahead of consumer AR in terms of maturity as said by Tuong Nguyen, who is principal research analyst at Gartner.
He goes on to say "We're really in the adolescence of AR and VR. We've had some time to test it, but it's still in its teenage years, so there are some growing pains to be expected. But we're already starting to see its potential."
The top three enterprise AR use cases right now include video guidance, design and collaboration and task itemization, according to Nguyen.
"For training, it's helpful for situations that are high risk" Nguyen said. "If it's expensive or dangerous to have someone training in a live environment, but you want them to at least know the muscle movement and the decisions they will need to make, you can have them do it in a virtual space, rather than in the physical world." Nguyen states this could include scenarios such as military surgery training, combat training or other emergency response training.
There are a number of products on the market aimed at enterprise adoption of VR/AR technology. A couple of examples are HTC Vive Pro and the Oculus for Business bundle. These can be used for enhancing worker productivity and job training in fields such as manufacturing and design, retail, transportation and healthcare.
Nguyen says "For any business, when implementing tech, it's either making you money or saving you money," and follows on to say "When you talk about employee training and use of immersive tech, it tends to be some type of cost savings, whether in the form of less accidents, higher accuracy rates, or fewer mistakes. That's the kind of benefit that the CIO should be expecting." With this being said, because these are interface technologies, success depends mostly on the task", he added.
Nguyen recommends doing some research and testing to see how these technologies can apply to your company. "Think about how it applies to solving certain problems, as an extension of tech" Nguyen said. "Don't just bring it in and say, let's see what we can do with this.”
The entertainment industry is still the main user of these technologies. Todd Richmond, IEEE member and director of the Mixed Reality Lab at the University of Southern California says "the bigger play long-term are the business verticals" and "Medical and education are going to outstrip entertainment with regards to uses for VR and AR."
The biggest use for AR/VR technologies in the future will be around telepresence, Richmond said. "It's the promise that has been on the horizon, of being able to telecommute in ways that are meaningful and productive," and states, "We're still not there yet. The immersive stuff is a new medium for communication and collaboration, and it takes time to figure out how to use a new medium effectively."
Richmond recommends that companies who are interested, seek out academic conferences to learn more about how it could fit into their current business structure. Richmond says "The trick for the enterprise is going to be figuring out when to make the leap, and when things are mature enough to move from it being a curiosity, and a set of experiments, to being a core part of their business"
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

November 12, 2019

Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies have been around for a while. The potential for these technologies are endless. Mining companies have embraced VR/AR for some time and are always looking to do more. Currently these technologies are, for example, reducing equipment maintenance costs and offering their personnel a safe way to train.
AR and VR technologies are being used widely at both the consumer and commercial levels. Companies like Microsoft and Google are developing their own VR/AR technologies and are competing for their market share. The VR/AR industry is predicted to be worth more than $150 billion worldwide by 2020.
Mining industries utilized VR/AR quite early, as the potential for training is ground breaking. Using these technologies for training not only saves companies money but has been proven that it can be a better way to train employees.
Mining operators have realised the potential to address many issues with VR/AR technology, with improvements in productivity, safety and machinery uptime to name just a few. For mining companies, AR offers training in the real world with helpful overlays. VR replaces the real world with a simulated training environment.
EMIMSAR, an EU funded project, is a system that allows miners to be able to view AR versions of complex equipment on helmet mounted displays. Using sensors to record and analyse temperatures, rates of acceleration and sample noise from sprockets. This allows staff to assess heavy duty components like gears and chains. This data is then given to a knowledge based maintenance system. When combined with background data on components, it creates real time virtual visualisations on the machinery which can be viewed by other miners while working on the same machine.
The EMIMSAR AR system has been developed and used to great success by Germany’s largest coal mining firm RAG, which used it for maintenance planning, loaders and belt conveyors.
Kumba Virtual Reality Centre, which opened in August 2015 has incorporated a 3D stereoscopic theatre and a 3D, 360° cylinder theatre. The 3D simulation creates true to detail mining conditions and creates scenarios such as underground rock falls, that is truly immersive experience for the user.
Rio Tinto has now partnered with New York based Bravo Media to custom design the Oculus Rift experience. It features a computer generated environment that allows the user to fly above the coast of Canada, before taking you for a tour down the Diavik diamond mine.
Grey Properjohn from Australian company Vix Technology wrote in a newsletter "The ability to mix virtual content with reality will provide countless opportunities to improve operational safety and efficiency, as well as bringing the corporate offices even closer to the operations on the ground by connecting people in ways never imagined before,"
He goes on to write "Imagine standing in an underground development heading and becoming visually aware of all the adjacent headings, slopes and declines in the immediate vicinity, or being able to virtualise the trends in ground features like fault-zones or stress-zones… Extend this to drilling from underground and you can virtually eliminate the potential to inadvertently intersect other existing openings.”
"The assessment of mining an open pit through underground workings takes on new meaning if you could actually 'see' the workings. Even from an office environment, users can be immersed in the underground operation tracking the locations of all people and assets within the mine in real-time."
These are just a few examples of how mining companies are using the VR/AR technology. Many more projects are in development that are sure to excite.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

September 19, 2019

“We always overestimate the change that will occur in the next two years and underestimate the change that will occur in the next ten. Don't let yourself be lulled into inaction.”
- Bill Gates
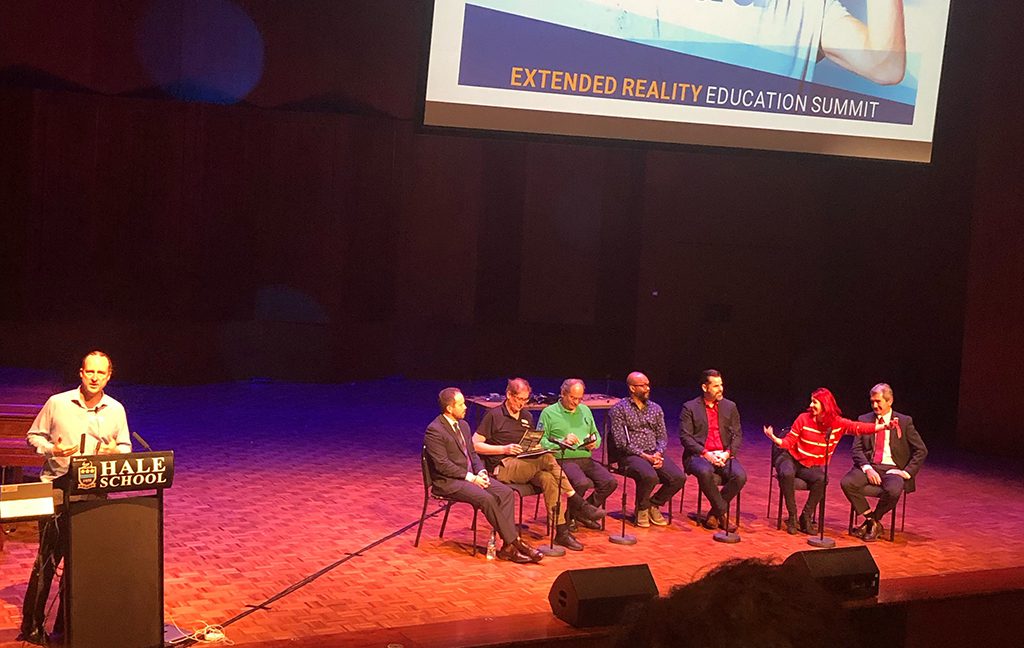
We were delighted to present the “Industry Perspective” at the inaugural XR.Edu Summit held at Hale School this week. iTRA’s Director, Mark Broome,showcased our experience and innovations to the room of educators giving them a perspective on the business cases for Extended Reality in the real world. We spoke with a number of people afterwards who recognised the value of giving students exposure to #VR #AR #XR and giving them projects with tangible applications.
Mark predicted in the next few years, as the hardware cost reduces and business cases become clearer, we will see an exponential rise in the use of XR applications across all industries. He rammed home his point with the example of mobile phones to highlight the adoption rate of technology when the elements align:
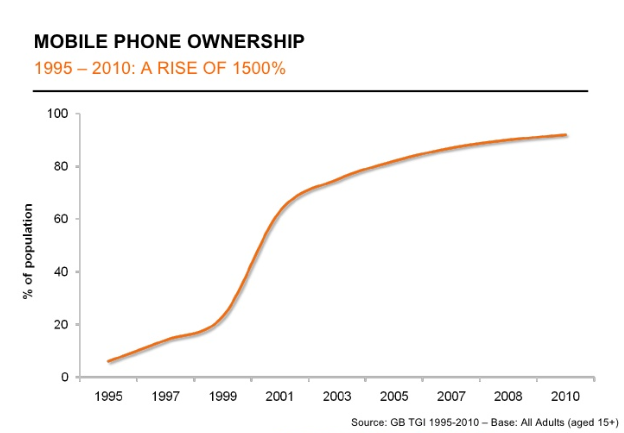
As early developers iTRA is fortunate to have long term clients that recognise the benefits of including VR training in their suite of tools to improve the skills of their workforce. We have been developing XR applications since 2017 and continue to identify areas within our clients’ businesses where tangible improvements can be made with VR or AR applications.
Our experience shows that VR is without doubt an ideal training tool for immersion in high risk work environments and a cost-effective alternative for all kinds of training for physical activity, such as use of fire extinguishers, driving, identification of objects, etc.
AR has enormous potential for improving efficiencies in operations and this has been proven by major companies who have adopted the technology, such as DHL, Toll, and Boeing. Our AR Tagging App is just one application, but AR in Inspection & Maintenance, Operations Training, Remote Collaboration and Working Guides are all areas where AR will save both time and money.
The XR.Edu Summit presentation was well received by the audience who were looking for inspiration to produce graduates who are ready for the real world – in an extended reality space.
Please contact us for more information on the use of XR applications within your organisation.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

September 3, 2019

You would think that having state of the art technology on the battlefield would give you a significant advantage? Well think again, as the more tech you use, the more likely your crew will be detected from the RF used to communicate. There is a saying that always rings true in the armed forces. “If your transmitting, you can be found”.
While on duty, armed forces are often equipped with many communication devices such as GPS, mobile devices, SOS beacon, hand-held radios, or Wi-Fi, with these devices emitting their own radio frequency traceable back to the sender. This means that a lot of personnel participating in active battles will have to turn off their devices to avoid detection as its important to be invisible to the enemy.
Currently to ensure transmitting devices are secure, soldiers use a handheld tablet weighing over 4 Kilograms. The device is equipped with a handheld radio to scan for and identify their own frequencies. While this device does come under the banner of portable, it’s still very heavy and can be a pain to use. Not only that, it forces the operator to take his/her eyes off the battlefield in order to scan, which can be risky in a live battle.
With the downfalls of the current technology, a Naval Information Warfare Center (NIWC) Atlantic team, is currently developing and testing a new transmission detection system that utilizes Augmented Reality technology. It projects visuals over the user’s real-world environment providing an accurate hands free way of detecting their own RF waves. This new system is dubbed ‘The Spectrum Hunter’
Operators have a few ways to use and communicate with this device, such as voice recognition technology, and can interpret physical hand gestures. This allows the user to easily locate and deactivate RF transmissions, but at the same time have an active eye on the field looking for danger.
In an article for Naval Information Warfare Center Atlantic Public Affairs, Sinclair says “The Spectrum Hunter system under development is hands-free. As the user packs a similar-but-smaller geolocator receiver in a backpack and wears a headset inside a helmet that allows them to ‘see’ images of RF waves on an augmented reality screen superimposed over heavy sunglasses,” and also adds “The helmet is fitted with a sunshade so the equipment operates outdoors.”
NIWC Atlantic Acting Executive Director Peter C. Reddy adds.“The sky is the limit for potential uses for Spectrum Hunter.” and “Augmented reality can enable an operator to more quickly and easily locate the source; this is a paradigm shift toward capabilities of the future.”
In the future, the Navy hopes to build on and expand the use of its Spectrum Hunter. In time it is hoped that this technology will be used to detect the enemies RF waves as well. “Our team is initially focusing on detecting handheld radios and will expand the scope later to detect cell phones and other devices,” Sinclair explains. “In the future, we plan to modify it to identify RF waves emitting from enemy forces.”
The prototype of The Spectrum Hunter was showcased last July at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, North Carolina. During this exercise, experts from more than 35 government agencies and industries were able to brainstorm potential insights on how they see this project and where it can go.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

August 27, 2019

Augmented Reality has been around for a while now, with there being lots of new uses for this technology, from mockup workplaces to state of the art simulations. It surely is time to utilize this technology in an office environment. Using the Magic Leap One with its CNN app, this combination can allow you to setup an AR space, anywhere, anytime.
Magic Leap One has been on the market for about a year now. Surprisingly this device hasn’t really hit the mainstream, at least not yet. One thing is for sure, every office could use a bit of livening up with some cool AR products. Magic Leap one is a viable tool for the average white-collar office worker.
The Magic Leap One offers an easy to use truly immersive experience, using wearable AR technology. It’s easy to see how tech like this can enhance your everyday experience of the world around you. Using this technology in the office can improve productivity just by making the most mundane tasks more enjoyable.
Generally an office space will consist of a whole lot of monitors, mice, keyboards and whiteboards enabling workers to multitask various activities. Now think about donning a headset and having everything you need at your fingertips at all times. Sure, it seems pretty unfamiliar to put something on your head and view the world around you in an altered state. But if you were to really think about it, it makes sense, as you can see exactly what is needed at any time using AR technology. This saves workers time and increases productivity.
The Magic Leap can be used with other users easily. One of its best features is its ability to put AR holograms in your vision that look pretty realistic. Unlike VR, which closes you off from the world, AR lets you remain engaged with real people and places. Also, although increasing numbers of white-collar workers are working remotely, the working world is still dominated by people in office spaces.
Magic Leap works best with a high speed internet connection, public wifi such as cafes lack the internet gusto needed. Also noted is that the headset gives off some heat in operation, but as long as your office is air conditioned this will not affect comfort in use. The Magic Leap also comes with a shoulder strap which is very useful when using the device for long periods of time.
The most important thing to consider when setting up a virtual office with the Magic Leap One, is figuring out which apps make the experience the best it possibly can be. Some apps that work well together are: the Cheddar news video streaming app, Clock app, Wallpaper app via Screens app, Gallery app, Avatar Chat and of course Helio (the AR web browser). When you put all these apps together you get a truly immersive and fun workspace.
Another useful feature of the Magic Leap One is the ability to force a particular screen to "follow" you wherever you go. The following functionality is in the menu of most Magic Leap apps and can be initialized by clicking on the front-facing bumper.
With these apps working together, the experience is deep and surprisingly non-distracting. An AR environment that can turn a normal, dull working space into a colorful center of activity.
If we want to talk about drawbacks, the main one would be its limited battery life, a common problem shared by all mobile devices. In an AR office setup battery life won't last much longer than 3 hours. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing as it's a good idea to take a break after a few hours. The Control device consumes much less power if you're not constantly using it, so it requires much fewer recharges. While on the subject of battery life, it can be inconvenient to have to open the main menu and navigate to the battery icon, just to find out how much power the device has left. Once the Magic Leap drops to 25% power left you will be shown a warning of low battery life.
The Magic Leap AR office setup may not be everyone's cup of tea, but for someone with a boring job or limited work space, this might just be the setup. It’s easy to see co-working spaces offering the Magic Leap One as an optional menu item, allowing visitors to create their own virtual space among unaffiliated workers. Because of the relatively opaque effect of the AR panels and the ability to plug a pair of normal headphones into the device, it’s easy to create a bubble of AR constructs amid a crowd of fellow co-working space users.
People are getting seasoned to the idea of wearing a headset, You won't necessarily get weird looks by wearing the Magic Leap One in a public setting, though you still might get the occasion look of “what’s that thing on your head?”. People really are now ready for the AR future.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

August 16, 2019
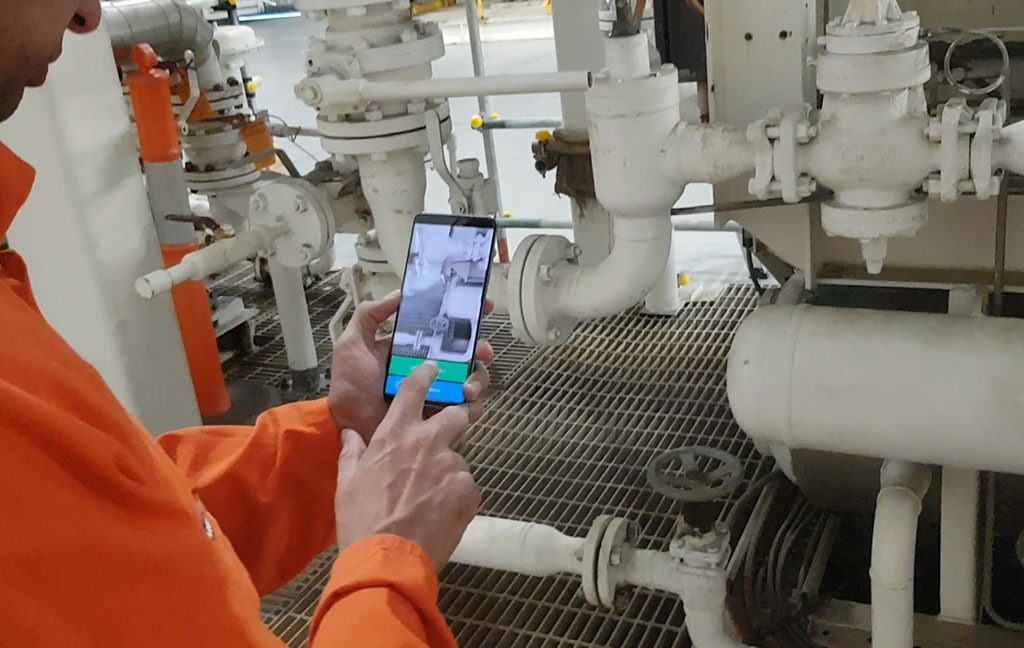

iTRA are in the development stage of a new App named “Tager” which allows the user to electronically tag items (hence the name). Currently, development is targeting a process to support and enhance the electronic PTW system and also as a potential replacement of QR codes.
The App can be used on any (intrinsically safe) mobile device, with Tag entries directly visible to the process controller / Permit Authority.
The App essentially works on item and environment recognition. Once the designated item is identified, the user applies the App (tap of a screen) with that “Tag” transferred directly to a database or control system.
Whilst the existing Permit to Work system remains essentially unchanged, Tager would add an additional layer of control. A Permit Authority, using a device, applies the Tag to the process, plant or equipment, linked to relevant supporting documentation. This Tag can only be applied and removed at the PTW site, not remotely.
The electronic Tag interfaces with the existing PTW but also locks out the process, plant or equipment. The process / plant / equipment cannot be re energised until the electronic Tag is removed by the Permit Authority.
Tager may also be used to enhance or replace the more traditional QR code. Tager would electronically interface with existing processes and not only provide direct visible access to information imbedded in a QR code but overcomes a significant QR Code weakness - longevity of the Code in harsh environments.
Early days, but the results are promising.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.

July 9, 2019

More and more we are seeing new uses for virtual and augmented reality, but this technology has been around for quite a few years in some form. Virtual reality is the term used to describe an immersive experience through a computer generated environment which doesn’t actually exist. Our senses give us the perception of how we view the world around us. Everything we know about reality comes from what we have learnt through our senses.
Virtual reality uses various technologies to create an all encompassing simulation of an environment, which can yield great results for learning and development. VR has been used with great results in the healthcare, science, research and training areas.

The use of virtual reality can be traced back to the mid 1800s. Charles Wheatstone researched the idea that the brain is processing two, two dimensional images to create depth of view, so we can perceive the world in three dimensions. The research concluded that viewing two images through a stereoscope provided a sense of immersion and depth.
Augmented reality on the other hand does not create a virtual world, but rather imposes holograms on the users environment. The term augmented reality came about in the 1990’s, with Thomas Caudel using the term to describe the head mounted displays that electricians wore whilst undertaking complex assembly work. Many new AR apps are being released, which are mixing computer generated images with the real life environment. AR Google Maps is a good example of what can be achieved for apps of this kind.
For Learning purposes, VR can be used to mimic the environment the student will be working in. This means the student can interact, manipulate objects or carry out a series of tasks, for the purpose of training and gaining experience. For example a mockup of a workplace.
Education is an area that has great applications and opportunities for virtual and augmented reality. Learning is conducted much more efficiently, is more engaging for the user and can be a fun experience too. Primarily these technologies have been seen in the gaming industry, but studies have shown using VR/AR in the training realm has significant benefits.
Virtual reality enables the student to enter a 360 degree video shot or immerse themselves in a 3D environment. A great example of this technology is the VR training for marine biologists. They can enter into the natural environment of the ocean all without stepping foot near a boat or the coast. The lecturer will activate a series of scenarios and wearing virtual reality glasses, the students can experience the actual environment. Virtual learning environments are also created in online education where students can send, create and manage coursework, as well as study digital material.
Over the last few years, VR has really taken center stage as a great innovation in the world of learning and eLearning. The delivery of this sort of training will have an upfront cost (from purchasing VR headsets and Smartphones for example).
Realistic Scenarios
The nature of virtual reality means that trainers can enhance learning content and create a remarkably interactive learning experience.
Mistakes
With virtual reality technology it does not matter if the student were to make a mistake, it’s just a part of the learning process. In certain training situations such as nursing for example, it would be impractical not to mention dangerous, for a student nurse or doctor to train on a real patient. With VR, trainers can replicate a real life scenario, but the trainee is safe knowing that they cannot harm a ‘virtual’ patient.
Suitable for different learning styles
This type of learning can really help people who benefit from a more tactile style of learning and who struggle with the theory side.
Resource Saving
Setting up training in a traditional training environment can be costly and take up a lot of room. VR offers trainees a safer environment, which can also use less floor space than a full sized mocked up environment. This space can also be converted to be utilized in another way while training is not in progress.
Innovative and Enjoyable
Elearning specialists are always looking for cutting edge ways to deliver their training and using virtual and augmented reality is making the whole learning experience more enjoyable and immersive. It can be used in many different scenarios, from customer service to teaching, healthcare and even engineering.
Integration
For the moment, it is quite difficult to convert all learning types to virtual and augmented reality, as it requires a lot of resources to convert and test VR/AR products. For this reason, careful consideration is required when choosing which courses to convert and where this technology will have the most benefit.

Costly
Even though there are virtual reality devices to suit all budgets, investing in VR for large scale training is a real wallet drain, particularly when the training needs to be delivered to many students or employees.
Training Locations
With traditional eLearning, a student can learn quite effectively and quietly sitting at a desk. With VR the trainee will need more room to function, so there is no risk of falling over desks or bumping into chairs. Due to this an employer or training provider will need to provide suitable space for the trainee and the VR equipment.
eLearning into the future
The future of eLearning is evolving and set to advance further, with VR and AR applications bringing two technologies that will enable this to happen. These technologies can facilitate the learning process in various ways, particularly in industries which involve more complex and/or high risk practices.
Connect with iTRA to discuss your next project.
Resources
Terms and ConditionsABN: 67119 274 181